|
Convert H264 to JPG/JPEG Sequence
|
JPG/JPEG is a commonly used method of lossy compression
for digital photography (image). The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing
a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves
10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.
H264 to JPG/JPEG Converter Software converts H264 to JPG/JPEG
sequence files. So, you could get every frame image of H264 in
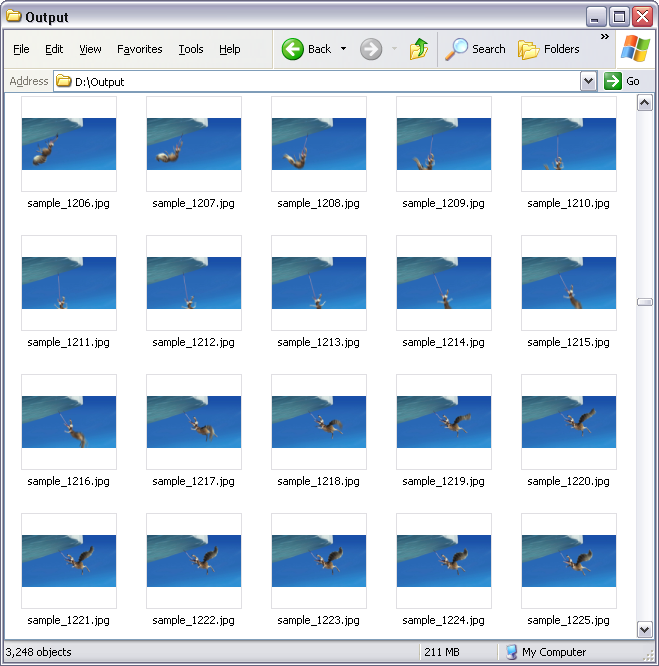
JPG/JPEG format. You can also set output frame rate and JPG/JPEG resolution in
the software. The output JPG/JPEG files look something like the following screen
shot.
The software also supports other formats and portable devices such as MP2, AC3, MPG, Windows Phone, WebM (VP8), Android Tablet, SWF,
etc. The software could convert M2TS to AMR, RM to MP2, DVD to MP3, WebM to AVI, 3G2 to AIFF, and so on.
H264 to JPG/JPEG Software supports batch conversion and, is compatible
with Windows 10/8/7/Vista/XP/2000.

What is H264?
H.264 is a codec used to create MP4 files. Its wide compatibility and range
of features has made it a popular encoder for videos. Constrained Baseline
Profile (CBP): Primarily for low-cost applications, this profile is most
typically used in videoconferencing and mobile applications. It corresponds
to the subset of features that are in common between the Baseline, Main,
and High Profiles. In early 1998, the Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG
- ITU-T SG16 Q.6) issued a call for proposals on a project called H.26L,
with the target to double the coding efficiency (which means halving the
bit rate necessary for a given level of fidelity) in comparison to any
other existing video coding standards for a broad variety of applications.
Also known as AVC (Advanced Video Coding, MPEG-4 Part 10), H.264 is actually
defined in an identical pair of standards maintained by different organizations,
together known as the Joint Video Team (JVT). H.264 is a new video codec
standard which can achieve high quality video in relatively low bitrates.
On the other hand, for spatial and quality bitstream scalability (i.e.
the presence of a sub-bitstream with lower spatial resolution/quality than
the main bitstream), the NAL (Network Abstraction Layer) is removed from
the bitstream when deriving the sub-bitstream. HTML5 adds two new tags
to the HTML standard: <video> and <audio> for direct embedding
of video and audio content into a web page. Controversies surrounding the
H.264 video compression standard stem primarily from its use within the
HTML5 Internet standard. The intent of the H.264/AVC project was to create
a standard capable of providing good video quality at substantially lower
bit rates than previous standards (i.e., half or less the bit rate of MPEG-2,
H.263, or MPEG-4 Part 2), without increasing the complexity of design so
much that it would be impractical or excessively expensive to implement.
What is JPG?
Standard computer file format for storing graphic images in a compressed
form for general use. JPEG images are compressed using a mathematical algorithm.
A variety of encoding processes can be used, depending on whether the user's
goal is the highest quality of image (lossless) or smallest file size (lossy).
The JPEG and GIF formats are the most commonly used graphics formats on
the Internet for lossy and lossless data compression, respectively. JPEG,
which stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group (the name of the group
that created the standard), is a commonly used lossy technique of compression
for color photographic images. An image in JPEG format has a '.jpg', '.jpeg',
or '.jpe', extension. A number of alterations to a JPEG image can be performed
losslessly (that is, without recompression and the associated quality loss)
as long as the image size is a multiple of 1 MCU block (Minimum Coded Unit)
(usually 16 pixels in both directions, for 4:2:0 chroma subsampling). Utilities
that implement this include jpegtran, with user interface Jpegcrop, and
the JPG_TRANSFORM plugin to IrfanView. Image files that employ JPEG compression
are commonly called "JPEG files", and are stored in variants
of the JIF image format. Most image capture devices (such as digital cameras)
that output JPEG are actually creating files in the Exif format, the format
that the camera industry has standardized on for metadata interchange.
On the other hand, since the Exif standard does not allow color profiles,
most image editing software stores JPEG in JFIF format, and also include
the APP1 segment from the Exif file to include the metadata in an almost-compliant
way; the JFIF standard is interpreted somewhat flexibly.
How to Convert H264 to JPG/JPEG Sequence?
- Free Download H264 to JPG/JPEG
Converter Software
- Install the Program by Step-by-step Instructions
- Launch H264 to JPG/JPEG Software
- Choose H264 Files
Click "Add Files" to choose H264 files.
Choose one or more H264 files you want to convert and then click Open.
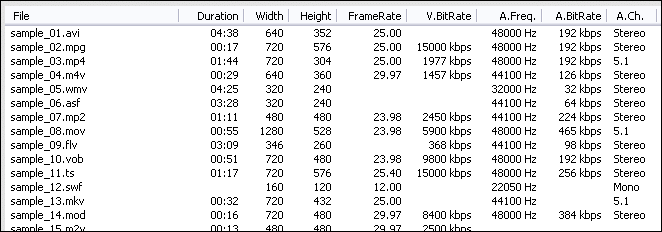
H264 to JPG/JPEG Software will open H264 files and get file information
of the file such as width, height, frame rate, video bit rate, audio sample rate,
audio bit rate, audio channels, and then display the information of H264 file
at conversion list.
- Choose Output Format
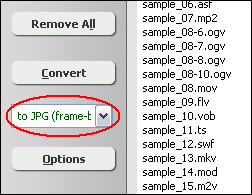
Click on combo-box of output format and then choose "to JPG (image sequence)".
- [Optional, for advanced user]
Set JPG Encoding Parameters
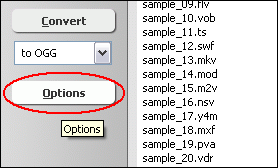
If you want to change JPG encoding parameters such as frame rate, video size,
aspect ratio, and so on, please click "Options".
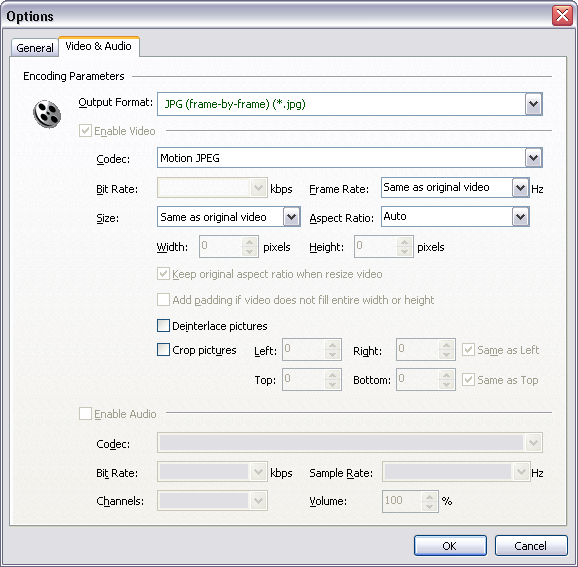
And then, switch to tab "Video & Audio" and choose "JPG
(image sequence)" at "Output Format", and then set options
for image encoding.
- Convert H264 to JPG/JPEG
Click "Convert" to convert H264 to JPG/JPEG sequence.
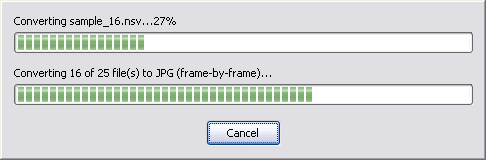
The software is converting H264 files to JPG/JPEG.
- View and Browse JPG/JPEG Files
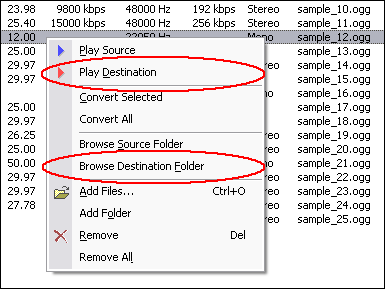
When conversion completes, you can right-click converted item and choose "Play
Destination" to view the first outputted JPG file; or choose "Browse
Destination Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the outputted JPG
files.
- Done
Top
H264 to JPG/JPEG Software is 100% clean and safe to
install. It's certified by major download sites.

Convert H264 to JPG/JPEG Related Topics:
|