|
Convert AVI to H.264
|
AVI to H.264 Converter Software converts AVI files to H.264. With
an easy-to-use interface, it makes AVI to H.264 conversion routine as easy
as 1-2-3, without knowledge of AVI and H.264. The converter helps any beginners
and experts to create high quality video files in minutes. This program encodes
AVI to H.264 with professional quality. The AVI to H.264 Converter Software enables
more people enjoy the advantage about this advanced video
coding. The H.264 is one of HTML5 video formats, you can also
put the H.264 video to your website.
The software could convert more than 100 media foramts to popular video formats
and portable devices such as 3G2, WMA, M4V, AU, OGM, SWF, MP3, etc. It could convert 3G2 to FLAC, M4V to Windows Phone, M4V to WebM (VP8), EVO to 3G2, MPEG to OGV,
and so on.
AVI to H.264 Converter Software supports batch conversion and,
is full compatible with 32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows 10/8/7/Vista/XP/2000.

What is AVI?
AVI stands for Audio Video Interleave, defined by Microsoft. For WAV audio
files, Broadcast Wave extensions were designed to standardize post-production
metadata, but an equivalent for AVI files has not emerged. AVI and codec
are inseparable. There are several competing approaches to including a
time code in AVI files, which affects usability of the format in film and
television post-production, although it is widely used. Each version of
Windows ships with a video player software (called Windows Media Player),
so that is not a problem. The problem is called the codec. AVI files can
be played by various video players, but the player must support the codec
used to encode the video data. It can also be seen with QuickTime and RealPlayer
(available for the Mac). The first sub-chunk is identified by the "hdrl"
tag. This sub-chunk is the file header and contains metadata about the
video, such as its width, height and frame rate. An AVI file takes the
form of a single chunk in a RIFF formatted file, which is then subdivided
into two mandatory "chunks" and one optional "chunk".
By way of the RIFF format, the audio-visual data contained in the "movi"
chunk can be encoded or decoded by software called a codec, which is an
abbreviation for (en)coder/decoder. AVI format is one of the oldest video
formtas. The third optional sub-chunk is identified by the "idx1"
tag which indexes the offsets of the data chunks within the file. Recent
files might be compressed with one or another codecs (like DivX and XviD).
It can also be seen with VLC Player, MPlayer, The KMPlayer. AVI was not
intended to contain video using any compression technique which requires
access to future video frame data beyond the current frame. Approaches
exist to support modern video compression techniques (such as MPEG-4) which
rely on this function, although this is beyond the intent of the original
specification and may cause problems with playback software which does
not anticipate this use.
What is H.264?
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC (Advanced Video Coding) is a standard for video
compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for
the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video.
The standard was developed jointly in a partnership of VCEG and MPEG, after
earlier development work in the ITU-T as a VCEG project called H.26L. The
final drafting work on the first version of the standard was completed
in May 2003. VCEG was chaired by Gary Sullivan (Microsoft, formerly PictureTel,
USA). As the term is used in the standard, a "level" is a specified
set of constraints indicating a degree of required decoder performance
for a profile. H.264 is a new video codec standard which can achieve high
quality video in relatively low bitrates. The Digital Video Broadcast project
(DVB) approved the use of H.264/AVC for broadcast television in late 2004.
For example, H.264 has been reported to give the same Digital Satellite
TV quality as current MPEG-2 implementations with less than half the bitrate,
with current MPEG-2 implementations working at around 3.5 Mbit/s and H.264
at only 1.5 Mbit/s. To ensure compatibility and problem-free adoption of
H.264/AVC, many standards bodies have amended or added to their video-related
standards so that users of these standards can employ H.264/AVC. Two profiles
were developed in the MVC work: Multiview High Profile supports an arbitrary
number of views, and Stereo High Profile is designed specifically for two-view
stereoscopic video. The JVT was (is) chaired by Gary Sullivan, Thomas Wiegand,
and Ajay Luthra (Motorola, USA). The Scalable Video Coding extensions were
completed in November 2007.
How to Convert AVI to H.264?
- Free Download
AVI to H.264 Converter Software
- Install the Program by Step-by-step Instructions
- Launch AVI to H.264 Converter Software
- Choose AVI Files
Click "Add Files" to choose AVI files.
Choose one or more AVI files you want to convert and then click Open.
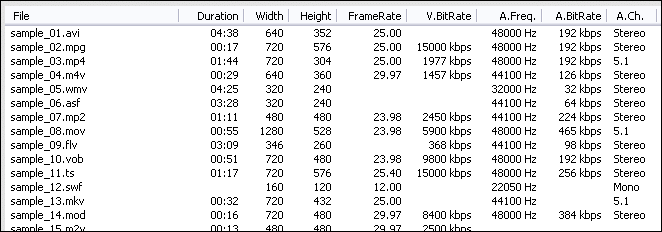
AVI to H.264 Converter Software will open AVI files and get file information
of the file such as width, height, frame rate, video bit rate, audio sample rate,
audio bit rate, audio channels, and then display the information of AVI file
at conversion list.
- Choose Output Format
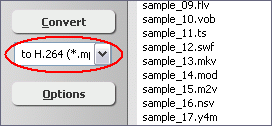
Click on combo box of output format and then choose "to H.264".
- [Optional, for advanced user]
Set H.264 Encoding Parameters
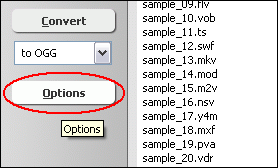
If you want to change H.264 encoding parameters such as bit rate, frame rate,
video size, and aspect ratio, please click "Options".
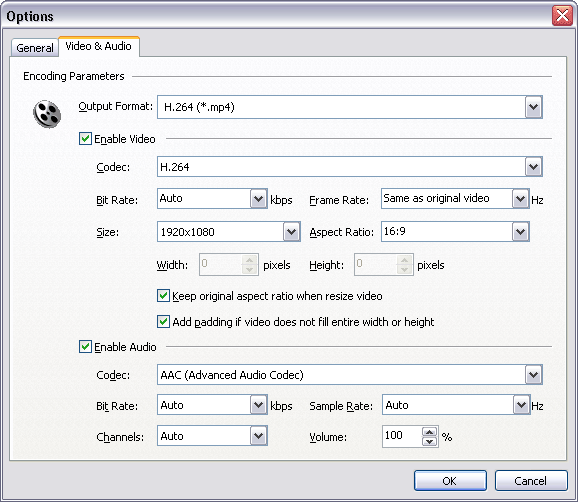
And then, switch to tab "Video & Audio" and choose "H.264
(*.mp4)" at "Output Format", and then set options for
video and audio.
- Convert AVI to H.264
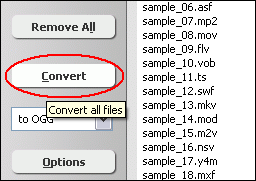
Click "Convert" to convert all AVI files in list to H.264 format.
The software is converting AVI files to H.264.
- Play & Browse
When conversion completes, you can right-click converted item and choose "Play
Destination" to play the outputted H.264 file; or choose "Browse
Destination Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the outputted H.264
file.
- Done
Top
AVI to H.264 Converter Software is 100% clean and safe to
install. It's certified by major download sites.

Convert AVI to H.264 Related Topics:
|